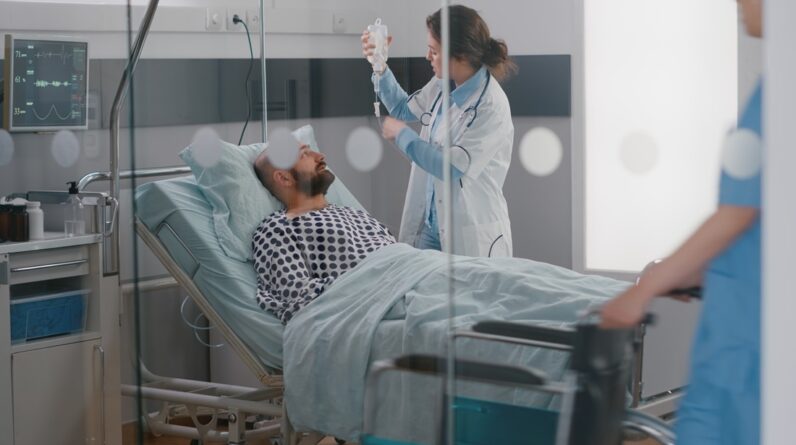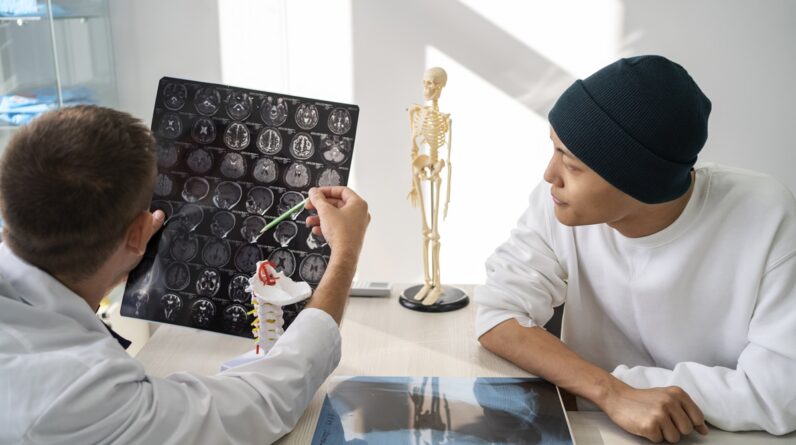
Neurological surgery, also known as neurosurgery, is a specialized field of medicine focused on diagnosing and treating conditions affecting the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. This branch of surgery combines intricate techniques with advanced technology to address a wide range of neurological disorders.
What is Neurological Surgery?
Neurological surgery involves surgical interventions to manage conditions such as brain tumors, spinal cord injuries, epilepsy, and vascular disorders like aneurysms. Neurosurgeons are trained to operate on the delicate structures of the nervous system, often employing sophisticated techniques and equipment to achieve the best outcomes.
Common Conditions Treated
- Brain Tumors: Neurosurgeons remove or reduce the size of tumors in the brain, aiming to minimize damage to healthy tissue and preserve neurological function.
- Spinal Disorders: Conditions like herniated discs, spinal stenosis, and spinal cord injuries can be treated through various surgical approaches to alleviate pain and restore function.
- Epilepsy: For patients with epilepsy that doesn’t respond to medication, surgical options like resection of the seizure focus or implantation of a neurostimulator may be considered.
- Vascular Malformations: Aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), and other vascular issues can be addressed through surgical techniques to prevent rupture or manage bleeding.
- Traumatic Injuries: Neurosurgery can treat severe brain and spinal cord injuries resulting from trauma, aiming to repair damage and optimize recovery.
Technological Advancements
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: Innovations such as endoscopic surgery allow for smaller incisions and reduced recovery times. These techniques use specialized instruments and cameras to navigate and treat neurological conditions with precision.
- Robotic Assistance: Robotic systems enhance the accuracy of neurosurgical procedures. Surgeons use robotic platforms to perform delicate operations with enhanced dexterity and control.
- Intraoperative Imaging: Real-time imaging techniques, such as intraoperative MRI or CT scans, provide surgeons with up-to-date visual information, improving the accuracy of tumor resection and other procedures.
- Neuro-navigation Systems: These systems use advanced imaging and tracking technologies to guide surgeons in real-time, ensuring precise targeting of surgical sites and minimizing damage to surrounding tissues.
Challenges and Considerations
- Complexity of Procedures: Neurosurgery involves intricate procedures that require a deep understanding of the nervous system. The proximity of critical structures means that even minor errors can have significant consequences.
- Recovery and Rehabilitation: Post-surgery recovery can vary greatly depending on the type of procedure and the patient’s overall health. Rehabilitation often involves physical therapy, occupational therapy, and sometimes speech therapy to regain lost functions.
- Risk Management: As with any surgery, there are risks involved, including infection, bleeding, and neurological deficits. Neurosurgeons must carefully weigh the potential benefits against these risks for each individual patient.
The Future of Neurological Surgery
The field of neurological surgery is rapidly evolving with ongoing research and technological advancements. Future directions include:
- Gene Therapy and Molecular Medicine: Research into gene therapy could lead to new treatments for genetic neurological disorders, potentially altering the course of diseases at a molecular level.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI and machine learning are being integrated into diagnostic tools and surgical planning, offering the potential for more accurate and personalized treatments.
- Regenerative Medicine: Stem cell research and tissue engineering hold promise for repairing damaged nervous tissue and restoring function in cases of injury or degenerative diseases.